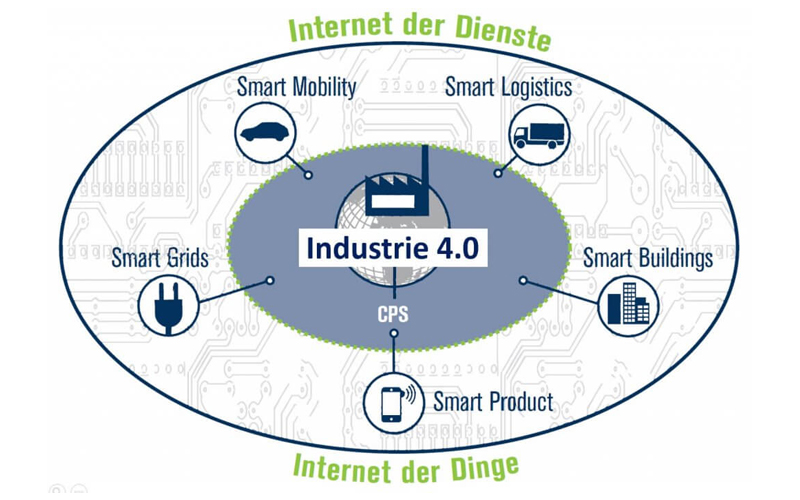
Industry 4.0 is the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the
Internet of things also cloud computing.Industry 4.0 creates what has been called a "smart factory". Within the modular structured smart factories, cyber-physical systems monitor physical processes, create a virtual copy of the physical world and make decentralized decisions. Over the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems communicate and cooperate with each other and withhumans in real time, and via the Internet of Services, both internal and cross-organizational services are offered and used by participants
of the value chain.
Some have compared Industrie 4.0 with the Fourth Industrial Revolution. However, the latter refers to a systemic transformationthat includes impact on civil society, governance structures, and human identity in addition to solely economic/manufacturing ramifications. The first
industrial revolution mobilised the mechanization of production using water and steam power; the second
ndustrial revolution then introduced mass production with the help of electric power, followed by the digital revolution and the use ofelectronics and IT to further automate production. The term "fourth industrial revolution" has been applied to significant technological
developments several times over the last 75 years, and is up for academic debate. Industrie 4.0, on the other hand, focuses
on manufacturing specifically in the current context, and thus is separate from the fourth industrial revolution in terms of scope.
Some examples for Industry 4.0 are machines which can predict failures and trigger maintenance processes autonomously or self-organized
logistics which react to unexpected changes in production.
There are differences between a typical traditional factory and an Industry 4.0 factory. In the current industry environment, providinghigh-end quality service or product with the least cost is the key to
success and industrial factories are trying to achieve as much performance as possible to increase their profit as well as their reputation. In this way, various data sources are available to provide worthwhile information about different aspects of the factory. In this stage, the utilization of data for understanding current operating conditions and detecting faults and failures is an important topic to research. e.g. in production, there are various commercial tools available to provide Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) information to factory management in order to highlight the root causes of problems and possible faults in the system. In contrast, in anIndustry 4.0 factory, in addition to condition monitoring and fault diagnosis, components and systems are able to gain self-awareness and
self-predictiveness, which will provide management with more insight on the status of the factory. Furthermore, peer-to-peer comparison and
fusion of health information from various components provides a precise health prediction in component and system levels and force
factory management to trigger required maintenance at the best possible time to reach just-in time maintenance and gain neazero downtime.
